Cloud Computing: The Bedrock of the Future
May 6, 2020
Summary
- Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing service over the Internet, which provides cost efficiency, scalability and diversity to cloud users
- With the increased adoption of cloud technology, the cloud computing industry is entering its growth phase of the industry life cycle
- The ability to allow remote work access and enhancement of other complementary technological industries have made cloud computing the digital transformative tool of the 21st century
- Investors can gain exposure to the cloud computing industry via SKYY, CLOU, WCLD and 2826.HK
Introduction
A company’s IT may be described as a key back-office function. It is involved in various business critical activities; hardware setup, data management, software installation, platform maintenance etc.
A robust IT infrastructure is vital in delivering better customer service and improving operational efficiency. However, IT resources require a significant cost on capital, time and labour, and are generally managed internally.
As such, companies are often seeking ways to streamline IT operations to compete more effectively in the digital business environment. Central to the business transformation is the emergence of cloud computing technology, which allows companies to lower their IT costs and enhance their computing infrastructure.
But what is cloud computing and why is it revamping businesses around the world?
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing services over the internet. Instead of buying, owning and maintaining physical IT infrastructure, companies can obtain IT services on an as-needed basis from cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (NASDAQ: AMZN) and Microsoft Azure (NASDAQ: MSFT).
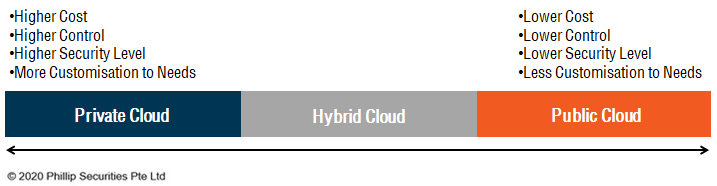
Cloud computing can be categorised according to their cloud locations.
| Cloud Location | Description |
| Private Cloud | Cloud computing resources that are used exclusively by a single organisation. A private cloud can be physically located at a company’s on-site infrastructure or outsourced to a cloud provider to host the private cloud.
Private clouds offer companies higher levels of control, security and customisation but come at a higher cost. |
| Hybrid Cloud | Hybrid clouds combine both private and public clouds, which allows the sharing and transferring of IT resources between them.
Hybrid clouds offer companies greater flexibility by allowing them to have deployment options between the two choices to optimise security level and fulfil business needs. |
| Public Cloud | Public clouds are solely owned and operated by third-party cloud providers. Public clouds allow the cloud providers to benefit from economies of scales whereby the same computing services can be sold to multiple users.
Greater scale allows for greater cost efficiencies, which can be passed on to cloud users as cost savings. |
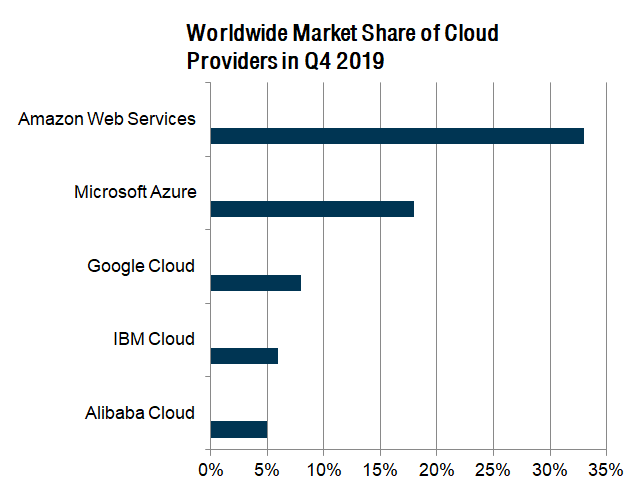
Today, the cloud computing industry is dominated by some of the largest technology companies in the world. None of the market leaders began as a pure play cloud company but each recognised the immense growth potential offered by the cloud computing industry. As a result, they devoted huge resources and technological expertise to capitalise on the structural demand change in IT consumers’ needs.
It is estimated that the global cloud computing market will reach US$623.3 billion by 2023, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18%.2
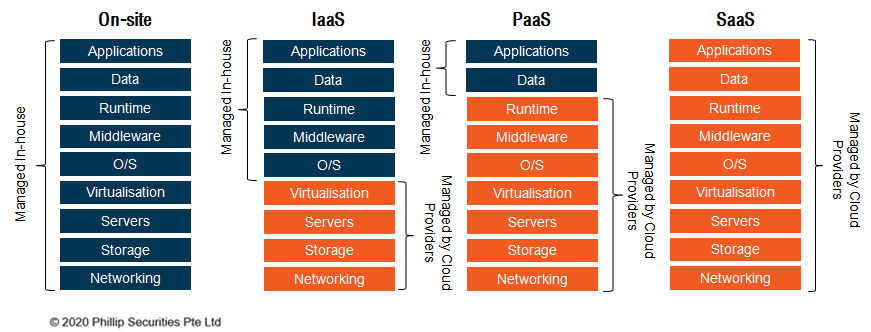
Types of Cloud Computing Services
There are three main types of cloud computing services; Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). They are often called the cloud computing stack because they build on top of one another.4
| Cloud Computing Service | Description |
| laaS | The most basic type of cloud computing service which is used for on-demand internet-based access to IT infrastructure like storage, server and networking facilities. |
| PaaS | Cloud computing services that provide an on-demand environment for cloud users to develop, test, deliver and manage software applications without the need to set up or manage the underlying IT infrastructure required for these functions. |
| SaaS | Cloud computing services that deliver software applications over the internet. With SaaS, cloud providers can host, manage and maintain the software application and underlying infrastructure. |
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing may seem abstract to us but it is actually present in our everyday lives although we may not notice it. For example, if you’ve ever hosted a blog or streamed a video online – that’s cloud computing technology in action.
Besides transforming our daily routines, cloud computing is also reshaping industries and businesses. To better illustrate this disruptive technology, we will discuss the underlying factors which are propelling the growth of the cloud computing industry.
Cost
Public cloud eliminates the capital expense of purchasing hardware and software, maintaining of computing infrastructure and hiring of IT personnel to deliver the required computing services. In addition, cloud computing reduces ongoing operating expenses like electricity bill for powering and cooling.5
A survey by Institute of Management Accountants found that lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is one of the main reasons why companies are relocating their business applications to the cloud. The financial responsibility for hardware and software upkeep is shifted from businesses to the cloud providers. Since the building and maintenance fees for on-site computing infrastructure provide no strategic advantage to a company’s core strategy, companies can divert their cost-savings and resources towards their core competencies.
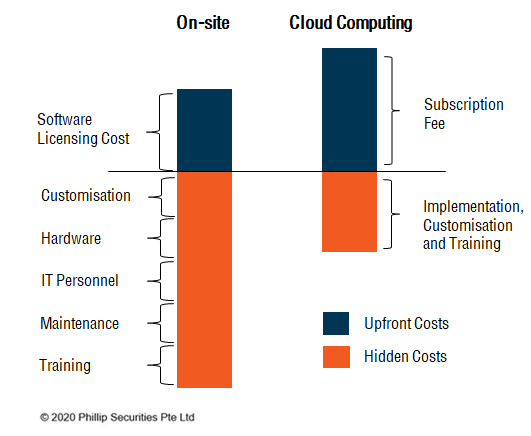
Global Scalability
Cloud computing grants companies the flexibility to scale elastically – the ability to adjust IT resources alongside with business’ growth. This prevents an oversupply of IT resources and redundant expenditures.
With cloud computing, companies can expand and deploy globally without the need to set up IT infrastructure in the respective countries. Cloud computing adopts a pay-as-you-go pricing model and companies do not have to incur substantial computing sunk cost in the expansion process. In the event that the overseas ventures fail, companies can simply withdraw operations and scale IT resources down from their cloud providers.
Service Innovation
The intense level of competition between cloud providers and technological advancement has reduced pricing for cloud users.6 As the price difference between cloud providers narrows, cloud service cost will be less of a differentiating factor when cloud users decide on their service providers.
Hence, the emphasis by cloud providers is now on service innovation to vie for the lucrative market share of the cloud consumer base. Instead of traditional cloud services like data storage or server provision, new cloud services are being introduced to cater for specialised customer requirements to overcome the problem of price commoditisation. New innovations can also create potential growth opportunities for cloud providers.
Once customised cloud services are integrated into a customer’s business processes, it becomes very difficult for the cloud user to switch to another provider. The personalised services allow for the deepening of the business relationships, through which the cloud providers can up sell additional products to existing client pool and drive up average revenue per customer.
The different needs and budgets of various industries have led to the creation of a vast diversity of cloud services. Examples of new cloud services may include data analytics, machine learning, data lakes, Internet of Things (IoT) etc.
Exchange Traded Funds
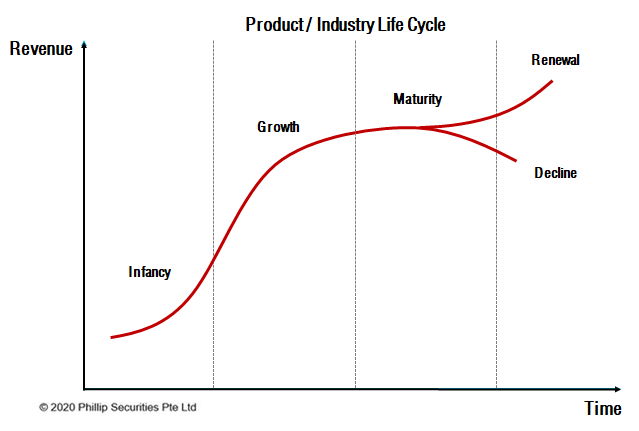
Cloud computing has predominately been around since the early 2000s. However, the lack of understanding and trust in cloud technology in the past have made many organisations reluctant in outsourcing their IT operations to third-party providers.
Suffice to say, the benefits of cloud computing have reduced its negative perception and led to the rapid adoption of the technology. As companies are increasingly receptive towards cloud computing, the industry is slowly breaking out of its infancy stage and entering its growth phase of the industry life cycle.7
Cloud computing thematic Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) are convenient investment vehicles for investors to gain exposure to the growth opportunities of the cloud computing industry.
| ETF | First Trust Cloud Computing ETF | Global X Cloud Computing ETF | WisdomTree Cloud Computing ETF | Global X China Cloud Computing ETF |
| Ticker | SKYY | CLOU | WCLD | 2826 |
| Exchange | NASDAQ | NASDAQ | NASDAQ | HKEx |
| AUM | USD 2.23 billion | USD 416 million | USD 44.8 million | HKD 521.63 million |
| Net Expense Ratio | 0.60% | 0.68% | 0.45% | 0.68% |
| Number of Holdings | 61 | 36 | 52 | 20 |
| Top 3 Holdings | – Amazon.com Inc (NASDAQ: AMZN) – Microsoft Corporation (NASDAQ: MSFT – Oracle Corporation (NYSE: ORCL) |
– Coupa Software Inc (NASDAQ: COUP) – Xero Ltd (ASX:XRO) – Shopify Inc Class A (NYSE:SHOP) |
– Zoom Video Communications Inc (NASDAQ:ZM) – Cloudflare Inc Class A (NASDAQ:NET) – Qualys Inc (NASDAQ:QLYS) |
– Winning Health Technology (SHE:300253) – Sangfor Technologies Inc (SHE:300454) – Yonyou Network Technology (SHE:600588) |
ETF information is accurate as of 14 April 2020
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of migrating business operations to cloud-based solutions. The ability to work remotely is an integral part of a business continuation plan and ensures that critical business functions are able to operate as usual in times of crisis.
Furthermore, the emergence of 5G technology, Internet of Things (IoT) and other technological innovations will create a greater demand for cloud services. Cloud computing enriches the capacity, functionality and flexibility of these industries and enhances the products and services that they can deliver to their end consumers.
To conclude, cloud computing may just be the digital transformative tool that provides the bedrock to revolutionise the entire value and supply chain of industries around the world.
References:
- [1] https://www.esds.co.in/blog/cloud-computing-types-cloud/
- [2] https://medium.com/swlh/the-growth-of-the-cloud-and-the-reasons-why-865f8fc8525f
- [3] https://www.statista.com/chart/18819/worldwide-market-share-of-leading-cloud-infrastructure-service-providers/
- [4] https://www.aerieconsulting.com/news/what-are-the-different-types-of-cloud-computing-services
- [5] https://blog.westmonroepartners.com/rain-down-cost-savings-with-cloud-based-business-applications/
- [6] https://www.computerweekly.com/news/4500270463/Public-cloud-competition-results-in-66-drop-in-prices-since-2013-research-reveals
- [7] https://www.zdnet.com/article/what-is-cloud-computing-everything-you-need-to-know-from-public-and-private-cloud-to-software-as-a/